This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2023) |
Imperial Abbey of Thorn | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1292–1794 | |||||||||
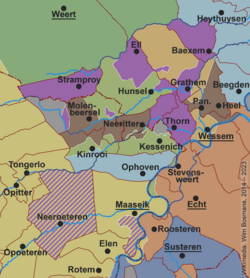 Territory of the Abbey of Thorn (purple), around 1700. | |||||||||
| Status | Imperial Abbey | ||||||||
| Capital | Thorn (Netherlands) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Dutch | ||||||||
| Government | Elective principality | ||||||||
| Abbess | |||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
• Founded | c. 975 | ||||||||
• Gained Imperial immediacy | 1292 | ||||||||
• Joined Council of Princes | 1793 | ||||||||
| 1794 | |||||||||
• Awarded to Netherlands | June 9, 1815 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Thorn Abbey or the Imperial Abbey of Thorn was an imperial abbey of the Holy Roman Empire in what is now the Netherlands. It was founded in the 10th century and remained independent until 1794, when it was occupied by French troops. The self-ruling abbey enjoyed imperial immediacy and belonged to the Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle.
At the time Thorn Abbey was invaded by the French revolutionaries in 1794, its territory was composed of three non-contiguous parts totaling 52.1 km2. In addition, the abbess shared rule over nearby areas totaling 35 km2. The abbey's territory was divided into four "quarters", each administered by two mayors. The population in 1796 was 2,975 inhabitants.
In 1797, the abbey was officially dissolved by the French. The Baroque interior survived the restoration but the spire was replaced with a massive neo-Gothic bell tower.[1]
