| Snake toxin and toxin-like protein | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
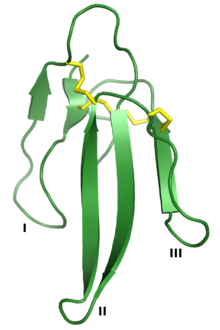 Erabutoxin A, a neurotoxin that is a member of the 3FTx superfamily. The three "fingers" are labeled I, II, and III, and the four conserved disulfide bonds are shown in yellow. Rendered from PDB: 1QKD.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Toxin_TOLIP | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00087 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0117 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR003571 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PS00272 | ||||||||
| CATH | 1qkd | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1qkd / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 53 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1txa | ||||||||
| CDD | cd00206 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Three-finger toxins (abbreviated 3FTx) are a protein superfamily of small toxin proteins found in the venom of snakes. Three-finger toxins are in turn members of a larger superfamily of three-finger protein domains which includes non-toxic proteins that share a similar protein fold. The group is named for its common structure consisting of three beta strand loops connected to a central core containing four conserved disulfide bonds. The 3FP protein domain has no enzymatic activity and is typically between 60-74 amino acid residues long.[2][3][4][5] Despite their conserved structure, three-finger toxin proteins have a wide range of pharmacological effects. Most members of the family are neurotoxins that act on cholinergic intercellular signaling; the alpha-neurotoxin family interacts with muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), the kappa-bungarotoxin family with neuronal nAChRs, and muscarinic toxins with muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs).[2]
- ^ Nastopoulos V, Kanellopoulos PN, Tsernoglou D (September 1998). "Structure of dimeric and monomeric erabutoxin a refined at 1.5 A resolution". Acta Crystallographica Section D. 54 (Pt 5): 964–74. Bibcode:1998AcCrD..54..964N. doi:10.1107/S0907444998005125. PMID 9757111.
- ^ a b Kini RM, Doley R (November 2010). "Structure, function and evolution of three-finger toxins: mini proteins with multiple targets". Toxicon. 56 (6): 855–67. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.07.010. PMID 20670641.
- ^ Hegde RP, Rajagopalan N, Doley R, Kini M (2010). "Snake venom three-finger toxins". In Mackessy SP (ed.). Handbook of venoms and toxins of reptiles. Boca Raton: CRC Press. pp. 287–302. ISBN 9781420008661.
- ^ Kessler P, Marchot P, Silva M, Servent D (August 2017). "The three-finger toxin fold: a multifunctional structural scaffold able to modulate cholinergic functions". Journal of Neurochemistry. 142 (Suppl 2): 7–18. doi:10.1111/jnc.13975. PMID 28326549.
- ^ Utkin Y, Sunagar K, Jackson T, Reeks T, Fry BG (2015). "Chapter 8: Three-finger toxins". In Fry B (ed.). Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery. Oxford University Press. pp. 218–227. ISBN 9780199309405.