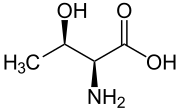
 Skeletal formula of L-threonine
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Threonine
| |||
| Other names
2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
| DrugBank |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.704 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| |||
| KEGG |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H9NO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 119.120 g·mol−1 | ||
| (H2O, g/dl) 10.6(30°),14.1(52°),19.0(61°) | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.63 (carboxyl), 10.43 (amino)[1] | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Threonine (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Threonine (symbol Thr or T)[2] is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form when dissolved in water), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as E. coli.[3] It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG).
Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices).
- ^ Dawson, R.M.C., et al., Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959.
- ^ "Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides". IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. 1983. Archived from the original on 9 October 2008. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ Raïs, Badr; Chassagnole, Christophe; Lettelier, Thierry; Fell, David; Mazat, Jean-Pierre (2001). "Threonine synthesis from aspartate in Escherichia coli cell-free extracts: pathway dynamics". Biochem J. 356 (Pt 2): 425–32. doi:10.1042/bj3560425. PMC 1221853. PMID 11368769.