 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tiapridal |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets), IM, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~75% (oral) (Tmax = 1 hour) |
| Protein binding | Negligible |
| Elimination half-life | 2.9–3.6 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (70% as unchanged tiapride) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.051.717 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
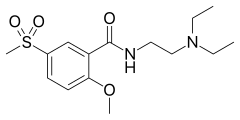
| Formula | C15H24N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 328.43 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tiapride is a drug that selectively blocks D2 and D3 dopamine receptors in the brain. It is used to treat a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders including dyskinesia, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, negative symptoms of psychosis, and agitation and aggression in the elderly.[2] A derivative of benzamide, tiapride is chemically and functionally similar to other benzamide antipsychotics such as sulpiride and amisulpride known for their dopamine antagonist effects.
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ Scatton B, Cohen C, Perrault G, Oblin A, Claustre Y, Schoemaker H, et al. (January 2001). "The preclinical pharmacologic profile of tiapride". European Psychiatry. 16 (Suppl 1): 29s–34s. doi:10.1016/s0924-9338(00)00526-5. PMID 11520476. S2CID 22686596.