| tibiae | |
|---|---|
 Position of tibia (shown in red) | |
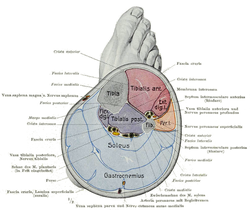 Cross section of the leg showing the different compartments (latin terminology) | |
| Details | |
| Articulations | Knee, ankle, superior and inferior tibiofibular joint |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | (os) tibia |
| MeSH | D013977 |
| TA98 | A02.5.06.001 |
| TA2 | 1397 |
| FMA | 24476 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The tibia (/ˈtɪbiə/; pl.: tibiae /ˈtɪbii/ or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.