Ticino | |
|---|---|
| Republic and Canton of Ticino Repubblica e Cantone Ticino (Italian) | |
|
| |
 | |
| Coordinates: 46°19′N 8°49′E / 46.317°N 8.817°E | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Capital | Bellinzona |
| Largest City | Lugano |
| Subdivisions | 115 municipalities, 8 districts |
| Government | |
| • Executive | Council of State (5) |
| • Legislative | Grand Council (90) |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,812.21 km2 (1,085.80 sq mi) |
| Population (December 2020)[2] | |
• Total | 350,986 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (320/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | CHF 33.181 billion (2021) |
| • Per capita | CHF 94,377 (2021) |
| ISO 3166 code | CH-TI |
| Highest point | 3,402 m (11,161 ft): Adula (Rheinwaldhorn) |
| Lowest point | 195 m (640 ft): Lake Maggiore |
| Joined | 1803 |
| Languages | Italian |
| HDI | 0.961 (2021)[4] very high · 3rd of 7 |
| Website | www |
Ticino (/tɪˈtʃiːnoʊ/ tih-CHEE-noh), sometimes Tessin (/tɛˈsiːn, tɛˈsæ̃/), officially[5] the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,[a] is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts and its capital city is Bellinzona. It is also traditionally divided into the Sopraceneri and the Sottoceneri, respectively north and south of Monte Ceneri. Red and blue are the colours of its flag.
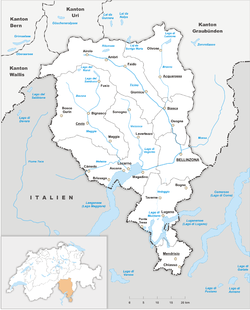
Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. It is one of the three large southern Alpine cantons, along with Valais and the Grisons. However, unlike all other cantons, it lies almost entirely south of the Alps and has no natural access to the Swiss Plateau. Through the main crest of the Gotthard and adjacent mountain ranges, it borders the canton of Valais to the northwest, the canton of Uri to the north and the canton of Grisons to the northeast; the latter canton being also the only one to share some borders with Ticino at the level of the plains. The canton shares international borders with Italy as well, including a small Italian enclave.
Named after the Ticino, its longest river, it is the only canton where Italian is the sole official language and represents the bulk of the Italian-speaking area of Switzerland along with the southern parts of the Grisons. In 2020, Ticino had a population of 350,986.[2] The largest city is Lugano, and the two other notable centres are Bellinzona and Locarno. While the geography of the Sopraceneri region is marked by the High Alps and Lake Maggiore, that of the Sottoceneri is marked by the Alpine foothills and Lake Lugano. The canton, which has become one of the major tourist destinations of Switzerland, distinguishes itself from the rest of the country by its warm climate, and its culture and gastronomy.
The land now occupied by the canton was annexed from Italian cities in the 15th century by various Swiss forces in the last transalpine campaigns of the Old Swiss Confederacy. In the Helvetic Republic, established in 1798, it was divided between the two new cantons of Bellinzona and Lugano. The Act of Mediation in 1803 saw these two cantons combine to form the modern canton of Ticino. Because of its unusual position, the canton relies on important infrastructure for connection with the rest of the country. The first major north–south railway link across the Alps, the Gotthard Railway, opened in 1882. In 2016, the Gotthard Base Tunnel was inaugurated, which finally provided a fully flat route through the Alps.
The GDP per capita of Ticino was 83,450 Swiss francs in 2020. Despite being below the Swiss average of 86,135 Swiss francs, it was still one of the wealthiest areas in Europe. Ticino also had the second highest life expectancy (85.2 years) in Europe in 2018.[6] The Human Development Index of 0.961 in 2021 was one of the highest found anywhere in the world.
- ^ Arealstatistik Land Cover - Kantone und Grossregionen nach 6 Hauptbereichen accessed 27 October 2017
- ^ a b "Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit". bfs.admin.ch (in German). Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB. 31 December 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ^ Statistik, Bundesamt für (27 October 2023). "Bruttoinlandsprodukt (BIP) nach Grossregion und Kanton - 2008-2021 | Tabelle". Bundesamt für Statistik (in German). Retrieved 24 July 2024.
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ^ Il Ticino in breve, ti.ch (official website of the canton). Retrieved 2021-01-25. ("Ticino is officially called the Republic and Canton of Ticino, its official language is Italian and its capital is Bellinzona")
- ^ swissinfo.ch, S. W. I. (30 September 2020). "Ticino has second-highest life expectancy in Europe". SWI swissinfo.ch. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).