| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tin(II) oxide
| |
| Other names
Stannous oxide
Tin monoxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.439 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| SnO | |
| Molar mass | 134.709 g/mol |
| Appearance | black or red powder when anhydrous, white when hydrated |
| Density | 6.45 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,080 °C (1,980 °F; 1,350 K)[1] |
| insoluble | |
| −19.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
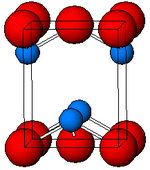
| Structure | |
| tetragonal | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
56 J·mol−1·K−1[2] |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−285 kJ·mol−1[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[3] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 2 mg/m3[3] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[3] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0956 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Tin sulfide Tin selenide Tin telluride |
Other cations
|
Carbon monoxide Silicon monoxide Germanium(II) oxide Lead(II) oxide |
| Tin dioxide | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tin(II) oxide (stannous oxide) is a compound with the formula SnO. It is composed of tin and oxygen where tin has the oxidation state of +2. There are two forms, a stable blue-black form and a metastable red form.
- ^ Tin and Inorganic Tin Compounds: Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 65, (2005), World Health Organization
- ^ a b Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0615". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).