| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.600 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Sn(NO3)4 | |
| Molar mass | 366.73 g/mol |
| Appearance | Silky Crystals |
| Density | 2.65 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 91 °C (196 °F; 364 K) |
| Boiling point | 98 °C (208 °F; 371 K) (decomposes) |
| Reacts | |
| Solubility | Soluble in carbon tetrachloride, chloroform |
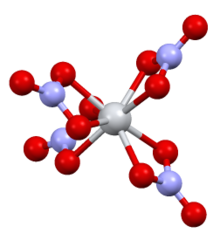
| Structure[3] | |
| Monoclinic | |
| P21/c | |
a = 7.80 Å, b = 13.85 Å, c = 10.23 Å
| |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H272, H314 | |
| P220, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tin(IV) nitrate is a salt of tin with nitric acid. It is a volatile white solid, subliming at 40 °C under a vacuum. Unlike other nitrates, it reacts with water to produce nitrogen dioxide.
- ^ "Tin(IV) Nitrate". American Elements. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ "Tin(IV) nitrate". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ C. D. Garner; D. Sutton; S. C. Wallwork (1967). "The crystal structures of anhydrous nitrates and their complexes. Part IV. Tin(IV) nitrate". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 1949–1954. doi:10.1039/J19670001949.