| Tinea cruris | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Eczema marginatum, crotch itch, crotch rot, dhobi itch, gym itch, jock itch, jock rot, scrot rot[1][2]: 303 |
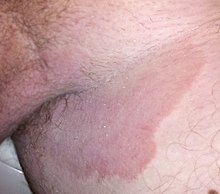 | |
| Tinea cruris on the groin of a man | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Itch, rash in groin |
| Risk factors |
|
| Diagnostic method | Microscopy and culture of skin scrapings |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention |
|
| Medication | Topical antifungal medications |
Tinea cruris (TC), also known as jock itch, is a common type of contagious, superficial fungal infection of the groin and buttocks region, which occurs predominantly but not exclusively in men and in hot-humid climates.[3][4]
Typically, over the upper inner thighs, there is an intensely itchy red raised rash with a scaly well-defined curved border.[3][4] It is often associated with athlete's foot and fungal nail infections, excessive sweating, and sharing of infected towels or sports clothing.[4][5][6] It is uncommon in children.[4]
Its appearance may be similar to some other rashes that occur in skin folds including candidal intertrigo, erythrasma, inverse psoriasis and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Tests may include microscopy and culture of skin scrapings.[7]
Treatment is with topical antifungal medications and is particularly effective if symptoms have recent onset.[5][6] Prevention of recurrences include treating concurrent fungal infections and taking measures to avoid moisture build-up including keeping the groin region dry, avoiding tight clothing and losing weight if obese.[8]
- ^ Rapini, R. P.; Bolognia, J. L.; Jorizzo, J. L. (2007). Dermatology. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ^ James, W. D.; Berger, T. G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ a b Lehrer, Michael (16 April 2019). "Jock itch". MedlinePlus. NLM / NIH.
- ^ a b c d Libby Edwards; Peter J. Lynch (2010). Genital Dermatology Atlas. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 67. ISBN 978-1-60831-079-1.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Rook2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Nadalo2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
DermnetNZ2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Wiederkehr2020was invoked but never defined (see the help page).