| Tinel's sign | |
|---|---|
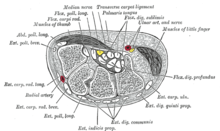 | |
| Transverse section across the wrist and digits. (The median nerve is the yellow dot near the center. The carpal tunnel is not labeled, but the circular structure surrounding the median nerve is visible.) | |
 | |
| A photograph conveying Tinel's sign being performed on the left foot to support the diagnosis of morton's neuroma. | |
| Specialty | Neurology, Plastic surgery |
| Differential diagnosis | Peripheral neuropathy, Radiculopathy, Plexopathy |
Tinel's sign (also Hoffmann-Tinel sign) is a way to detect irritated nerves. It is performed by lightly tapping (percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve.[1][2] Percussion is usually performed moving distal to proximal.[2] It is named after Jules Tinel.[3][4][5]
It is a potential sign of carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome,[6] anterior tarsal tunnel syndrome[7][8] and symptomatic neuroma.[9]
- ^ Gujar, Bansari; Flores, Raymond H. (2015-01-01), Hochberg, Marc C.; Silman, Alan J.; Smolen, Josef S.; Weinblatt, Michael E. (eds.), "81 - Entrapment neuropathies and compartment syndromes", Rheumatology (Sixth Edition), Philadelphia: Content Repository Only!, pp. 671–682, ISBN 978-0-323-09138-1, retrieved 2020-10-29
- ^ a b Lim, Aymeric Y. T.; Sebastin, Sandeep J. (2012-01-01), Chung, Kevin C.; Yang, Lynda J. -S.; McGillicuddy, John E. (eds.), "CHAPTER 14 - Clinical examination and diagnosis", Practical Management of Pediatric and Adult Brachial Plexus Palsies, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 173–197, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4377-0575-1.00014-9, ISBN 978-1-4377-0575-1, retrieved 2020-10-29
- ^ Tinel, J. (1978) The "tingling sign" in peripheral nerve lesions (Translated by EB Kaplan). In: M. Spinner M (Ed.), Injuries to the Ma jor Branches of Peripheral Nerves of the Forearm. (2nd ed.) (pp 8–13). Philadelphia: WD Saunders Co
- ^ Tinel, J. (1915) Le signe du fourmillement dans les lésions des nerfs périphériques. Presse médicale, 47, 388–389
- ^ Tinel, J., Nerve wounds. London: Baillère, Tindall and Cox, 1917
- ^ Waldman, Steven D.; Campbell, Robert S. D., eds. (2011-01-01), "CHAPTER 114 - Cubital Tunnel Syndrome", Imaging of Pain, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders: 289–290, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4377-0906-3.00114-0, ISBN 978-1-4377-0906-3, retrieved 2020-10-29
- ^ Waldman, Steven D.; Campbell, Robert S. D., eds. (2011-01-01), "CHAPTER 164 - Anterior Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome", Imaging of Pain, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders: 421–423, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4377-0906-3.00164-4, ISBN 978-1-4377-0906-3, retrieved 2020-10-29
- ^ Stephen, David J. G.; Choy, Gregory W.; Fam, Adel G. (2010-01-01), Lawry, George V.; Kreder, Hans J.; Hawker, Gillian A.; Jerome, Dana (eds.), "The Ankle and Foot", Fam's Musculoskeletal Examination and Joint Injection Techniques (Second Edition), Philadelphia: Mosby, pp. 89–101, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-06504-7.10007-7, ISBN 978-0-323-06504-7, retrieved 2020-10-29
- ^ Wolvetang, Nicolaas H. A.; Lans, Jonathan; Verhiel, Svenna H. W. L.; Notermans, Bo J. W.; Chen, Neal C.; Eberlin, Kyle R. (June 2019). "Surgery for Symptomatic Neuroma: Anatomic Distribution and Predictors of Secondary Surgery". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 143 (6): 1762–1771. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000005664. ISSN 0032-1052. PMID 30907815.