 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lanvis, Tabloid, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a682099 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30% (range 14% to 46%) |
| Metabolism | Intracellular |
| Elimination half-life | 80 minutes (range 25–240 minutes) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.299 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
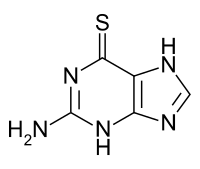
| Formula | C5H5N5S |
| Molar mass | 167.19 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Tioguanine, also known as thioguanine or 6-thioguanine (6-TG) or tabloid is a medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).[2] Long-term use is not recommended.[2] It is given by mouth.[2]
Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, liver problems and inflammation of the mouth.[2][3] It is recommended that liver enzymes be checked weekly when on the medication.[2] People with a genetic deficiency in thiopurine S-methyltransferase are at higher risk of side effects.[3] Avoiding pregnancy when on the medication is recommended.[2] Tioguanine is in the antimetabolite family of medications.[3] It is a purine analogue of guanine and works by disrupting DNA and RNA.[4]
Tioguanine was developed between 1949 and 1951.[5][6] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[7]
- ^ "Product monograph brand safety updates". Health Canada. February 2024. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f British National Formulary: BNF 69 (69th ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. pp. 588, 592. ISBN 978-0-85711-156-2.
- ^ a b c "Tioguanine 40 mg Tablets – Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) – (eMC)". www.medicines.org.uk. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 21 December 2016.
- ^ Baca QJ, Coen DM, Golan DE (2011). "Principles of antimicrobial and antineoplastic therapy". In Golan DE, Tashjian AH, Armstrong EJ (eds.). Principles of Pharmacology: The Pathophysiologic Basis of Drug Therapy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 686. ISBN 978-1-60831-270-2. Archived from the original on 2016-12-21.
- ^ Dubler E (1996). "Metal Complexes of Sulfur-Containing Purine Derivatives". In Sigel A, Sigel H (eds.). Metal Ions in Biological Systems. Vol. 32: Interactions of Metal Ions with Nucleotides: Nucleic Acids, and Their Constituents. CRC Press. p. 302. ISBN 978-0-8247-9549-8. Archived from the original on 2016-12-21.
- ^ Landau R, Achilladelis B, Scriabine A (1999). "Ch. 6. Clinical champions as critical determinants of drug development.". Pharmaceutical Innovation: Revolutionizing Human Health. Chemical Heritage Foundation. p. 342. ISBN 978-0-941901-21-5. Archived from the original on 2016-12-21.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.