| Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 2.3.2.13 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 80146-85-6 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
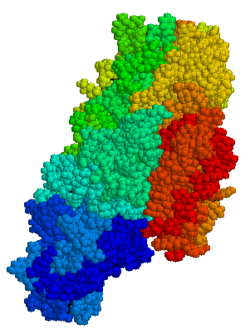
Tissue transglutaminase (abbreviated as tTG or TG2) is a 78-kDa, calcium-dependent enzyme (EC 2.3.2.13) of the protein-glutamine γ-glutamyltransferases family (or simply transglutaminase family).[5][6] Like other transglutaminases, it crosslinks proteins between an ε-amino group of a lysine residue and a γ-carboxamide group of glutamine residue, creating an inter- or intramolecular bond that is highly resistant to proteolysis (protein degradation). Aside from its crosslinking function, tTG catalyzes other types of reactions including deamidation, GTP-binding/hydrolyzing, and isopeptidase activities.[7] Unlike other members of the transglutaminase family, tTG can be found both in the intracellular and the extracellular spaces of various types of tissues and is found in many different organs including the heart, the liver, and the small intestine. Intracellular tTG is abundant in the cytosol but smaller amounts can also be found in the nucleus and the mitochondria.[6] Intracellular tTG is thought to play an important role in apoptosis.[8] In the extracellular space, tTG binds to proteins of the extracellular matrix (ECM),[9] binding particularly tightly to fibronectin.[10] Extracellular tTG has been linked to cell adhesion, ECM stabilization, wound healing, receptor signaling, cellular proliferation, and cellular motility.[6]
tTG is the autoantigen in celiac disease, a lifelong illness in which the consumption of dietary gluten causes a pathological immune response resulting in the inflammation of the small intestine and subsequent villous atrophy.[11][12][13] It has also been implicated in the pathophysiology of many other diseases, including such as many different cancers and neurogenerative diseases.[14]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000198959 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000037820 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Kiralywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Klockwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Facchianowas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
McConkeywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Lortat-Jacobwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Akimovwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM (December 2002). "Transglutaminases: nature's biological glues". The Biochemical Journal. 368 (Pt 2): 377–96. doi:10.1042/BJ20021234. PMC 1223021. PMID 12366374.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
DiRaimondowas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Sabatinowas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Király R, Csosz E, Kurtán T, Antus S, Szigeti K, Simon-Vecsei Z, Korponay-Szabó IR, Keresztessy Z, Fésüs L (December 2009). "Functional significance of five noncanonical Ca2+-binding sites of human transglutaminase 2 characterized by site-directed mutagenesis". The FEBS Journal. 276 (23): 7083–96. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07420.x. PMID 19878304. S2CID 21883387.