This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2014) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Orinase |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682481 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablet) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 96% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2C19-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 4.5 to 6.5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.541 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
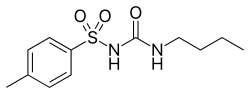
| Formula | C12H18N2O3S |
| Molar mass | 270.35 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 128.5 to 129.5 °C (263.3 to 265.1 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tolbutamide is a first-generation potassium channel blocker, sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic medication. This drug may be used in the management of type 2 diabetes if diet alone is not effective. Tolbutamide stimulates the secretion of insulin by the pancreas.
It is not routinely used due to a higher incidence of adverse effects compared to newer, second-generation sulfonylureas, such as Glibenclamide. It generally has a short duration of action due to its rapid metabolism, so is safe for use in older people.
It was discovered in 1956.[1]
- ^ Walker SR (2012). Trends and Changes in Drug Research and Development. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 109. ISBN 978-94-009-2659-2.