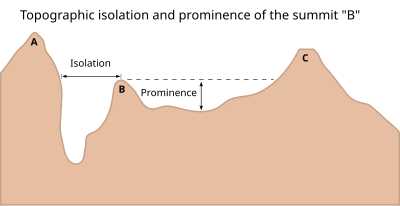
A - Nearest higher neighbour
The topographic isolation of a summit is the minimum distance to a point of equal elevation, representing a radius of dominance in which the peak is the highest point. It can be calculated for small hills and islands as well as for major mountain peaks and can even be calculated for submarine summits. Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth, has an undefined isolation, since there are no higher points to reference.[1]
Because topographic isolation can be difficult to determine, a common approximation is the distance to a peak called the nearest higher neighbour (NHN).[2]
- ^ Kirmse, Andrew; de Ferranti, Jonathan (December 2017). "Calculating the prominence and isolation of every mountain in the world". Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment. 41 (6): 788–802. doi:10.1177/0309133317738163. Retrieved 8 May 2024.
- ^ Nearest higher neighbour in glossary on www.peakbagger.com