 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Demadex, Tortas, Wator |
| Other names | Torsemide, Torsemide (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601212 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intraveneous |
| Drug class | Loop diuretic |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80-90% |
| Protein binding | Highly bound (>99%). |
| Metabolism | Liver (80%) |
| Elimination half-life | 3.5 hours; Cirrhosis: 7-8 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.924 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
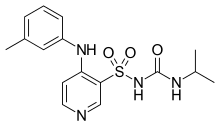
| Formula | C16H20N4O3S |
| Molar mass | 348.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Torasemide, also known as torsemide, is a diuretic medication used to treat fluid overload due to heart failure, kidney disease, and liver disease. It is a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure.[1] It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.[1]
Common side effects include headache, increased urination, diarrhea, cough, and dizziness.[1] Other side effects may include hearing loss and low blood potassium.[1] Torasemide is a sulfonamide and loop diuretic.[1] Use is not recommended in pregnancy or breastfeeding.[2] It works by decreasing the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys.[1]
Torasemide was patented in 1974 and came into medical use in 1993.[3] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[4] It is available as a generic medication.[2] In 2022, it was the 184th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.[5][6]
- ^ a b c d e f "Torsemide Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ a b British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 227–228. ISBN 978-0-85711-338-2.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 458. ISBN 978-3-527-60749-5.
- ^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Torsemide Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.