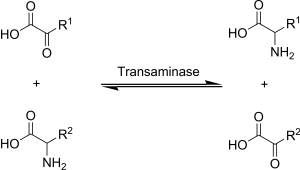
Transamination is a chemical reaction that transfers an amino group to a ketoacid to form new amino acids.This pathway is responsible for the deamination of most amino acids. This is one of the major degradation pathways which convert essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids (amino acids that can be synthesized de novo by the organism).
Transamination in biochemistry is accomplished by enzymes called transaminases or aminotransferases. α-ketoglutarate acts as the predominant amino-group acceptor and produces glutamate as the new amino acid.
Glutamate's amino group, in turn, is transferred to oxaloacetate in a second transamination reaction yielding aspartate.