| Triangle wave | |
|---|---|
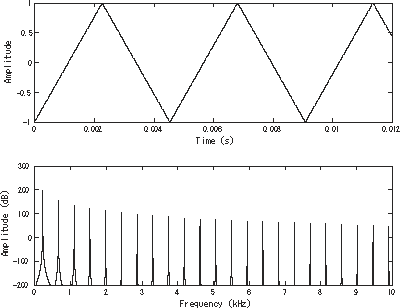 A bandlimited triangle wave[1] pictured in the time domain (top) and frequency domain (bottom). The fundamental is at 220 Hz (A3). | |
| General information | |
| General definition | |
| Fields of application | Electronics, synthesizers |
| Domain, codomain and image | |
| Domain | |
| Codomain | |
| Basic features | |
| Parity | Odd |
| Period | 1 |
| Specific features | |
| Root | |
| Derivative | Square wave |
| Fourier series | |
A triangular wave or triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape. It is a periodic, piecewise linear, continuous real function.
Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, the higher harmonics roll off much faster than in a square wave (proportional to the inverse square of the harmonic number as opposed to just the inverse).
- ^ Kraft, Sebastian; Zölzer, Udo (5 September 2017). "LP-BLIT: Bandlimited Impulse Train Synthesis of Lowpass-filtered Waveforms". Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx-17). 20th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx-17). Edinburgh. pp. 255–259.


![{\displaystyle \left[-1,1\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/79566f857ac1fcd0ef0f62226298a4ed15b796ad)


