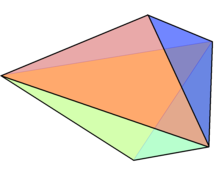
| Triangular bipyramid | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Bipyramid Deltahedra Johnson J11 – J12 – J13 |
| Faces | 6 triangles |
| Edges | 9 |
| Vertices | 5 |
| Vertex configuration | |
| Symmetry group | |
| Dihedral angle (degrees) | As a Johnson solid:
|
| Dual polyhedron | triangular prism |
| Properties | convex, composite, face-transitive |
A triangular bipyramid is a hexahedron with six triangular faces constructed by attaching two tetrahedra face-to-face. The same shape is also known as a triangular dipyramid[1][2] or trigonal bipyramid.[3] If these tetrahedra are regular, all faces of a triangular bipyramid are equilateral. It is an example of a deltahedron, composite polyhedron, and Johnson solid.
Many polyhedra are related to the triangular bipyramid, such as similar shapes derived from different approaches and the triangular prism as its dual polyhedron. Applications of a triangular bipyramid include trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry which describes its atom cluster, a solution of the Thomson problem, and the representation of color order systems by the eighteenth century.

