| Triceps | |
|---|---|
 Triceps brachii seen from behind. | |
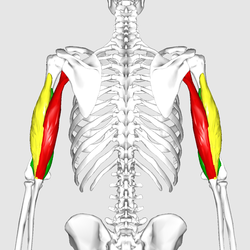 Triceps brachii seen from behind. Three different colors represent three different bundles which compose triceps. Long head. Lateral head. Medial head. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Long head: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula Lateral head: above the radial groove Medial head: below the radial groove |
| Insertion | Olecranon process of ulna |
| Artery | Deep brachial artery, posterior circumflex humeral artery (long head only) |
| Nerve | Radial nerve |
| Actions | Extends forearm, long head extends, adducts arm, extends shoulder |
| Antagonist | Biceps brachii muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus triceps brachii |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.019 |
| TA2 | 2471 |
| FMA | 37688 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head.[1] It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint (straightening of the arm).
- ^ Casadei, Kyle; Kiel, John; Freidl, Michael (2020). "Triceps Tendon Injuries". Current Sports Medicine Reports. 19 (9): 367–372. doi:10.1249/JSR.0000000000000749. PMID 32925376. S2CID 221567814.