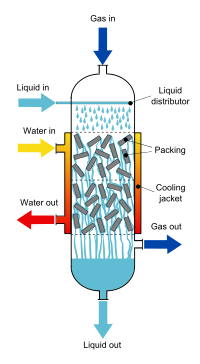
A trickle-bed reactor (TBR) is a chemical reactor that uses the downward movement of a liquid and the downward (co-current) or upward (counter-current) movement of gas over a packed bed of (catalyst) particles. It is considered to be the simplest reactor type for performing catalytic reactions where a gas and liquid (normally both reagents) are present in the reactor and accordingly it is extensively used in processing plants. Typical examples are liquid-phase hydrogenation, hydrodesulfurization, and hydrodenitrogenation in refineries (three phase hydrotreater) and oxidation of harmful chemical compounds in wastewater streams or of cumene in the cumene process.[1][2][3]
Also in the treatment of waste water trickle bed reactors are used where the required biomass resides on the packed bed surface.
- ^ Chaudhari, R. V.; Ramachandran, P. A. (March 1980). "Three phase slurry reactors". AIChE Journal. 26 (2): 177–201. doi:10.1002/aic.690260202.
- ^ Satterfield, Charles N. (March 1975). "Trickle-bed reactors". AIChE Journal. 21 (2): 209–228. doi:10.1002/aic.690210202.
- ^ Fogler, H. Scott (2006). Elements of chemical reaction engineering (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education International/Prentice Hall PTR. p. 850. ISBN 0130473944.