| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Diethylethanamine | |||
| Other names
(Triethyl)amine
Triethylamine (no longer IUPAC name[1]) | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | TEA[2] | ||
| 605283 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.064 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | triethylamine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1296 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties[5] | |||
| C6H15N | |||
| Molar mass | 101.193 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal | ||
| Density | 0.7255 g mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | −114.70 °C; −174.46 °F; 158.45 K | ||
| Boiling point | 88.6 to 89.8 °C; 191.4 to 193.5 °F; 361.7 to 362.9 K | ||
| 112.4 g/L at 20 °C[3] | |||
| Solubility | miscible with organic solvents | ||
| log P | 1.647 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 6.899–8.506 kPa | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
66 μmol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.75 (for the conjugate acid) (H2O), 9.00 (DMSO)[4] | ||
| -81.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.401 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
216.43 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−169 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−4.37763 to −4.37655 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H302, H312, H314, H332 | |||
| P210, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −15 °C (5 °F; 258 K) | ||
| 312 °C (594 °F; 585 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.2–8% | ||
Threshold limit value (TLV)
|
2 ppm (8 mg/m3) (TWA), 4 ppm (17 mg/m3) (STEL) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
| ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
1425 ppm (mouse, 2 hr)[7] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 25 ppm (100 mg/m3)[6] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
None established[6] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
200 ppm[6] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related amines
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
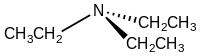
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation.[8][9] It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base.
- ^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 671. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ X. Bories-Azeau, S. P. Armes, and H. J. W. van den Haak, Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2348 PDF
- ^ "MSDS - 471283". www.sigmaaldrich.com. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
David Evans Research Groupwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ The Merck Index (11th ed.). 9582.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0633". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Triethylamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Ethanolamine Compounds (MEA, DEA, TEA And Others)". Safe Cosmetics. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- ^ "tetraethylammonium | Ligand page | IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY". www.guidetopharmacology.org. Retrieved 2020-06-17.


