| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(Trimethylammonio)acetate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3537113 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.174 |
| EC Number |
|
| 26434 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Betaine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
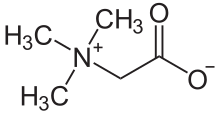
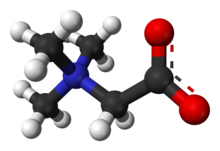
| C5H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 117.146 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K)[1] (decomposes) |
| Soluble | |
| Solubility | Methanol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.84 |
| Pharmacology | |
| A16AA06 (WHO) | |
| License data | |
| By mouth | |
| Legal status | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related amino acids
|
Glycine Methylglycine Dimethylglycine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Trimethylglycine is an amino acid derivative that occurs in plants. Trimethylglycine was the first betaine discovered; originally it was simply called betaine because, in the 19th century, it was discovered in sugar beets (Beta vulgaris subsp. vulgaris).[6]
- ^ Acheson RM, Bond GJ (1956). "52. Addition reactions of heterocyclic compounds. Part II. Phenanthridine and methyl acetylenedicarboxylate in methanol". J. Chem. Soc. 1956: 246. doi:10.1039/JR9560000246.
- ^ "Notice of Amendment: Betaine removed from the Prescription Drug List (PDL)". Health Canada. 6 January 2023. Retrieved 3 January 2024.
- ^ "Cystadane- betaine powder, for solution". DailyMed. 3 October 2019. Archived from the original on 4 August 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2022.
- ^ "Cystadane EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 1 July 2022. Retrieved 29 July 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ "Amversio EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 21 February 2022. Archived from the original on 30 July 2022. Retrieved 29 July 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ Schiweck H, Clarke M, Pollach G. "Sugar". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a25_345.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.