| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
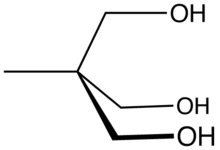
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.968 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12O3 | |
| Molar mass | 120.15 g/mol |
| Density | 1.22 g/mL |
| Melting point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 150 °C (302 °F; 423 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Trimethylolethane (TME) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(CH2OH)3. This colorless solid is a triol, as it contains three hydroxy functional groups. More specifically, it features three primary alcohol groups in a compact neopentyl structure. Its esters are known for their resistance to heat, light, hydrolysis, and oxidation. More important than TME and closely related is trimethylolpropane (TMP).
