| Abbreviation | TPM |
|---|---|
| Status | Published |
| Year started | 2009 |
| Latest version | ISO/IEC 11889:2015 2015 |
| Organization | Trusted Computing Group, ISO/IEC JTC 1 |
| Domain | Secure cryptoprocessor |
| Website | ISO/IEC 11889-1:2015, ISO/IEC 11889-2:2015, ISO/IEC 11889-3:2015, ISO/IEC 11889-4:2015 |
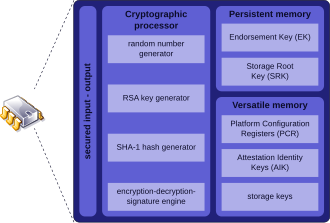
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard ISO/IEC 11889. Common uses are to verify platform integrity (to verify that the boot process starts from a trusted combination of hardware and software), and to store disk encryption keys.
One of Windows 11's operating system requirements is TPM 2.0 implementation. Microsoft has stated that this is to help increase security against firmware attacks.[1]
The bloat of functions was criticised, especially random number generation.[2]
- ^ Warren, Tom (2021-06-25). "Why Windows 11 is forcing everyone to use TPM chips". The Verge. Retrieved 2021-11-13.
- ^ Sen, Sayan (2023-08-03). "Linus Torvalds seems frustrated with AMD Ryzen fTPM bugs and issues, suggests disabling". Neowin. Retrieved 2024-10-23.