 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Heptin, Heptadrine, Tuamine |
| Other names | Tuamine; 2-Aminoheptane; 2-Heptanamine; 1-Methylhexylamine |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.233 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
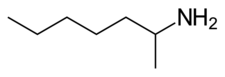
| Formula | C7H17N |
| Molar mass | 115.220 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 0.766 g/mL g/cm3 |
| |
| |
Tuaminoheptane (INN, BAN; brand names Heptin, Heptadrine, Tuamine; also known as tuamine and 2-aminoheptane) is a sympathomimetic agent and vasoconstrictor which was formerly used as a nasal decongestant.[2][3][4] It is still used in France as a nasal decongestant but its use is not recommended by the health authorities due to the lack of evidence of its effectiveness. It has also been used as a stimulant.[5][6]
Tuaminoheptane has been found to act as a reuptake inhibitor and releasing agent of norepinephrine, which may underlie its decongestant and stimulant effects.[7][8][6] It is an alkylamine.[6] The chemical structure of the drug differs from that of other norepinephrine releasing agents, such as the phenethylamines, which, in contrast to tuaminoheptane, have an aromatic ring in their structure.[8] Tuaminoheptane is also a skin irritant and can cause contact dermatitis via inhibition of volume-regulated anion channels, which limits its usefulness as a decongestant.[9]
Tuaminoheptane is on the 2011 list of prohibited substances published by the World Anti-Doping Agency.[5]
- ^ "tuamine - Compound Summary". PubChem. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 25 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ^ Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 623–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ Morton IK, Hall JM (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 282–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ^ Nickerson M, Dresel PE (September 1958). "Adrenergic drugs and their antagonists". Postgraduate Medicine. 24 (3): 246–256. doi:10.1080/00325481.1958.11692208. PMID 13591086.
- ^ a b Docherty JR (June 2008). "Pharmacology of stimulants prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA)". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (3): 606–622. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.124. PMC 2439527. PMID 18500382.
- ^ a b c Thevis M, Sigmund G, Geyer H, Schänzer W (March 2010). "Stimulants and doping in sport". Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America. 39 (1): 89–105, ix. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2009.10.011. PMID 20122452.
- ^ Delicado EG, Fideu MD, Miras-Portugal MT, Pourrias B, Aunis D (August 1990). "Effect of tuamine, heptaminol and two analogues on uptake and release of catecholamines in cultured chromaffin cells". Biochemical Pharmacology. 40 (4): 821–825. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(90)90322-c. PMID 2386550.
- ^ a b Schlessinger A, Geier E, Fan H, Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK, Giacomini KM, Sali A (September 2011). "Structure-based discovery of prescription drugs that interact with the norepinephrine transporter, NET". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (38): 15810–15815. Bibcode:2011PNAS..10815810S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1106030108. PMC 3179104. PMID 21885739.
- ^ Raoux M, Colomban C, Delmas P, Crest M (June 2007). "The amine-containing cutaneous irritant heptylamine inhibits the volume-regulated anion channel and mobilizes intracellular calcium in normal human epidermal keratinocytes". Molecular Pharmacology. 71 (6): 1685–1694. doi:10.1124/mol.106.033324. PMID 17384225. S2CID 29565968.