| Tube-dwelling spiders Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Segestria florentina | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Segestriidae Simon, 1893 |
| Diversity | |
| 5 genera, 160 species | |
| |
Tube-dwelling spiders (Segestriidae) are a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1893.[1] It consists of five genera, two large and widespread, Segestria and Ariadna, and three smaller genera, Citharoceps, Gippsicola and Indoseges.[2] They are haplogyne spiders, related to the Dysderidae and placed in clade or superfamily Dysderoidea.
Members of this family are easily recognized because their first three pairs of legs are arranged forward instead of two and they have six eyes instead of eight, arranged in a semicircle.[1] The leg structure appears to be an adaptation for living in silken tubes. Unlike those of the atypical tarantulas, these tubes may branch and are often built in tree bark fissures, as well as under stones.
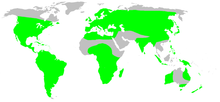
Both Segestria and Ariadna live in North America, South America, Eurasia, Africa and New Zealand, though Ariadna also lives in Australia.[2]