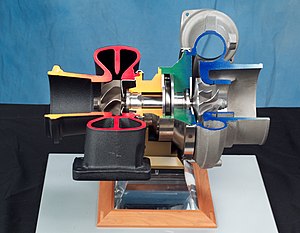
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.[1][2]
The current categorisation is that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases, whereas a supercharger is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft).[3] However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger.[4]
- ^ Nice, Karim (4 December 2000). "How Turbochargers Work". Auto.howstuffworks.com. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
- ^ [1] Archived 26 March 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Automotive handbook (6th ed.). Stuttgart: Robert Bosch. 2004. p. 528. ISBN 0-8376-1243-8. Retrieved 6 June 2022.
- ^ "The Turbosupercharger and the Airplane Power Plant". Rwebs.net. 30 December 1943. Retrieved 3 August 2010.