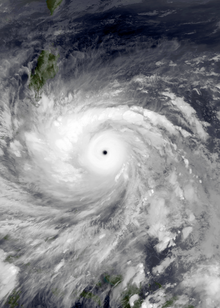
 Haiyan near peak intensity while approaching the Philippines on November 7 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | November 3, 2013 |
| Dissipated | November 11, 2013 |
| Violent typhoon | |
| 10-minute sustained (JMA) | |
| Highest winds | 230 km/h (145 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 895 hPa (mbar); 26.43 inHg |
| Category 5-equivalent super typhoon | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/JTWC) | |
| Highest winds | 315 km/h (195 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 895 hPa (mbar); 26.43 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 6,352 total |
| Injuries | 28,781 |
| Missing | 1,071 |
| Damage | >$2.99 billion (2013 USD) (Costliest in Philippine history) |
| Areas affected | Guam, Caroline Islands, Philippines, South China, Vietnam, Taiwan |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 2013 Pacific typhoon season | |
| History
Response Other wikis | |
Typhoon Haiyan, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Yolanda, was one of the most powerful tropical cyclones ever recorded. Upon making landfall, Haiyan devastated portions of Southeast Asia, particularly the Philippines.[1] It is one of the deadliest typhoons on record in the Philippines,[2] killing at least 6,300 people in the region of Visayas alone.[3] In terms of JTWC-estimated 1-minute sustained winds, Haiyan is tied with Meranti in 2016 for being the second strongest landfalling tropical cyclone on record, only behind Goni of 2020. Haiyan was also the most intense tropical cyclone worldwide in 2013.
The 30th named storm, thirteenth typhoon, and fifth super typhoon of the 2013 Pacific typhoon season, Haiyan originated from an area of low pressure several hundred kilometers east-southeast of Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia on November 2. Tracking generally westward, environmental conditions favored tropical cyclogenesis and the system developed into a tropical depression on the following day. After becoming a tropical storm and being named Haiyan at 00:00 UTC on November 4, the system began a period of rapid intensification that brought it to typhoon intensity by 18:00 UTC on November 5. By November 6, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) assessed the system as a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS); the storm passed over the island of Kayangel in Palau shortly after attaining this strength.
The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) estimated the average ten-minute sustained winds at 235 km/h (146 mph) and gusts up to 275 km/h (171 mph) at landfall over Guiuan, Eastern Samar. Haiyan continued to intensify; at 12:00 UTC on November 7, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) upgraded the storm's maximum ten-minute sustained winds to a peak of 230 km/h (145 mph). The Hong Kong Observatory put the storm's maximum ten-minute sustained winds at 285 km/h (175 mph)[4] prior to landfall in the central Philippines, while the China Meteorological Administration (CMA) estimated the maximum two-minute sustained winds at the time to be around 78 m/s (280 km/h or 175 mph). At the same time, the JTWC estimated the system's one-minute sustained winds at 315 km/h (195 mph), unofficially making Haiyan the strongest tropical cyclone ever observed based on wind speed, a record which would later be surpassed by Hurricane Patricia in 2015 at 345 km/h (215 mph).[5]
Haiyan is also tied with Meranti in 2016, Goni in 2020 and Surigae in 2021 as the most intense tropical cyclone in the Eastern Hemisphere by 1-minute sustained winds; several others have recorded lower central pressure readings. At 20:40 UTC on November 7, the eye of the typhoon made its first landfall in the Philippines at Guiuan, Eastern Samar at peak strength. Gradually weakening, the storm made five additional landfalls in the country before emerging over the South China Sea. Turning northwestward, the typhoon eventually struck northern Vietnam as a severe tropical storm on November 10. Haiyan was last noted as a tropical depression by the JMA on the following day.
The first warning noted for Haiyan was in November 3, when a storm warning arose in the Federated States of Micronesia, specifically in the Chuuk Lagoon, Losap, and Poluwat, gradually expanding to other towns as well. Warnings rose for a second time in Micronesia, before being discontinued. In the Philippines, PAGASA raised Signal No. 1 on November 6, before the landfall of Haiyan. More provinces were included, until Signal No. 4, the highest warning, was raised. Other preparations were made, such as class suspensions and evacuations. In China, an emergency was declared in three provinces, causing vessels to be brought back to shore. In Vietnam, the highest emergency level was announced, causing thousands of people to be evacuated.
In Micronesia, heavy rains scattered in most of the places, causing one canoe house and three other houses to be destroyed. Other than houses, much trees were downed. In Palau, houses were also destroyed. Power outages were reported, with a total of 69 people being displaced. In Taiwan, eight people died by strong waves. One person was also declared missing in Hong Kong. In Southern China, extensive flooding appeared, killing 30 people and destroying 900 homes. In Vietnam, heavy rains battered the country, killing 18 people and injuring 93.
The typhoon caused catastrophic destruction in the Visayas, particularly in the islands of Samar and Leyte. According to UN officials, about 11 million people were affected and many were left homeless; many people are still missing as a result of this storm.[6]
Due to its extensive deaths and damages, the name Haiyan was retired in 2014 and replaced with Bailu. It was first used in the 2019 season.
- ^ Why Typhoon Haiyan Caused So Much Damage (Report). NPR. November 11, 2013. Archived from the original on May 22, 2014. Retrieved April 21, 2014.
- ^ Typhoon Haiyan death toll rises over 5,000 (Report). BBC. November 22, 2013. Archived from the original on November 22, 2013. Retrieved November 22, 2013.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
NDRRMCwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Tropical Cyclones in 2013". December 18, 2015. Archived from the original on February 4, 2016. Retrieved December 18, 2015.
- ^ Mersereau, Dennis. "At 200 MPH, Hurricane Patricia Is Now the Strongest Tropical Cyclone Ever Recorded". The Vane. Archived from the original on October 23, 2015. Retrieved May 29, 2016.
- ^ "Tacloban: City at the centre of the storm". BBC. November 12, 2013. Archived from the original on November 13, 2013. Retrieved November 13, 2013.