This article about biology may be excessively human-centric. (October 2017) |
| Ulnar artery | |
|---|---|
 Palm of (corrected) right hand, showing position of skin creases and bones, and surface markings for the volar arches. | |
 Front of right upper extremity, showing surface markings for bones, arteries, and nerves. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Brachial artery |
| Branches | Anterior ulnar recurrent artery posterior ulnar recurrent artery common interosseous artery (volar, dorsal, recurrent interosseous artery) muscular artery volar carpal dorsal carpal deep volar superficial volar arch |
| Vein | Ulnar vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria ulnaris |
| MeSH | D017535 |
| TA98 | A12.2.09.041 |
| TA2 | 4655 |
| FMA | 22796 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
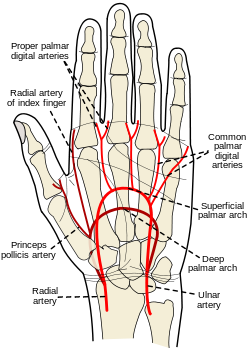
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.
Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein or veins, the ulnar vein or ulnar veins.
The ulnar artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial, begins a little below the bend of the elbow in the cubital fossa, and, passing obliquely downward, reaches the ulnar side of the forearm at a point about midway between the elbow and the wrist. It then runs along the ulnar border to the wrist, crosses the transverse carpal ligament on the radial side of the pisiform bone, and immediately beyond this bone divides into two branches, which enter into the formation of the superficial and deep volar arches.