Upper Galilee
| |
|---|---|
 A lemon orchard in the Galilee | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 32°59′N 35°24′E / 32.983°N 35.400°E | |
| Part of | |
| Native name | |
| Highest elevation | 1,208 m (3,963 ft) |
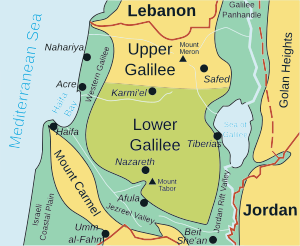
The Upper Galilee (Hebrew: הגליל העליון, HaGalil Ha'Elyon; Arabic: الجليل الأعلى, Al Jaleel Al A'alaa) is a geographical region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Part of the larger Galilee region, it is characterized by its higher elevations and mountainous terrain. The term "Upper Galilee" is ancient, and has been in use since the end of the Second Temple period. From a political perspective, the Upper Galilee is situated within the administrative boundaries of the Northern District of Israel.
The Upper Galilee is known for its natural beauty, including lush landscapes, Mediterranean forests, and scenic vistas. Significant natural sites include Nahal Amud and the Keshet Cave. It's also an area where vineyards and wineries thrive, producing quality wines. Mount Meron stands as the highest point in the area, reaching an elevation of 1,208 meters above sea level. Safed is a main city in the region and also hosts an artists' quarter that was a major center of Israeli art.[1][2]
Although historical definitions encompass parts of southern Lebanon within the boundaries of the Upper Galilee, the Lebanese government does not use the term "Galilee" for any part of its territory.