| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
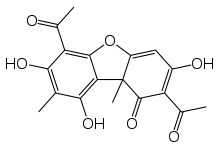
| IUPAC name
2,6-Diacetyl-7,9-dihydroxy-8,9b-dimethyldibenzo[b,d]furan-1,3(2H,9bH)-dione
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.310 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H16O7 | |
| Molar mass | 344.319 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 204 °C (399 °F; 477 K) |
| <0.001 g/L (25°C)[1] | |
| Solubility in acetone | 0.077 g/L[1] |
| Solubility in ethyl acetate | 0.088 g/L[1] |
| Solubility in furfural | 0.732 g/L[1] |
| Solubility in furfuryl alcohol | 0.121 g/L[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Usnic acid is a naturally occurring dibenzofuran derivative found in several lichen species with the formula C18H16O7. It was first isolated by German scientist W. Knop in 1844[2] and first synthesized between 1933 and 1937 by Curd and Robertson.[3] Usnic acid was identified in many genera of lichens including Usnea, Cladonia, Hypotrachyna, Lecanora, Ramalina, Evernia, Parmelia and Alectoria. Although it is generally believed that usnic acid is exclusively restricted to lichens, in a few unconfirmed isolated cases the compound was found in kombucha tea and non-lichenized ascomycetes.[4][5]
At normal conditions, usnic acid is a bitter, yellow, solid substance.[6] It is known to occur in nature in both the d- and l-forms as well as a racemic mixture. Salts of usnic acid are called usnates (e.g. copper usnate).
- ^ a b c d e O'Neil, Maryadele J.; Merck Sharp and Dohme Research Laboratories, eds. (2001). The Merck index: an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals (13th ed.). Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck. p. 1762. ISBN 978-0-911910-13-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Knop, W (1844). "Chemisch-physiologische Untersuchung uber die Flechten". Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 49 (2): 103–124. doi:10.1002/jlac.18440490202.
- ^ Robertson, A.; Curd, F. H. (1933). "277. Usnic acid. Part III. Usnetol, usnetic acid, and pyrousnic acid". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 1173. doi:10.1039/jr9330001173.
- ^ Cocchietto, Moreno; Skert, Nicola; Nimis, Pier; Sava, Gianni (2002). "A review on usnic acid, an interesting natural compound". Naturwissenschaften. 89 (4): 137–146. Bibcode:2002NW.....89..137C. doi:10.1007/s00114-002-0305-3. ISSN 0028-1042. PMID 12061397. S2CID 11481018.
- ^ Blanc, Philippe J. (1996). "Characterization of the tea fungus metabolites". Biotechnology Letters. 18 (2): 139–142. doi:10.1007/BF00128667. ISSN 0141-5492. S2CID 34822312.
- ^ Michael Ash; Irene Ash (2004). Handbook of preservatives. Synapse Info Resources. p. 5856. ISBN 978-1-890595-66-1. Retrieved 5 August 2010.