This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2007) |
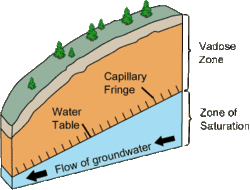
The vadose zone, also termed the unsaturated zone, is the part of Earth between the land surface and the top of the phreatic zone, the position at which the groundwater (the water in the soil's pores) is at atmospheric pressure ("vadose" is from the Latin word for "shallow"). Hence, the vadose zone extends from the top of the ground surface to the water table.
Water in the vadose zone has a pressure head less than atmospheric pressure, and is retained by a combination of adhesion (funiculary groundwater), and capillary action (capillary groundwater). If the vadose zone envelops soil, the water contained therein is termed soil moisture. In fine grained soils, capillary action can cause the pores of the soil to be fully saturated above the water table at a pressure less than atmospheric. The vadose zone does not include the area that is still saturated above the water table, often referred to as the capillary fringe. [1]
Movement of water within the vadose zone is studied within soil physics and hydrology, particularly hydrogeology, and is of importance to agriculture, contaminant transport, and flood control. The Richards equation is often used to mathematically describe the flow of water, which is based partially on Darcy's law. Groundwater recharge, which is an important process that refills aquifers, generally occurs through the vadose zone from precipitation.
- ^ Freeze, R.A. and Cherry, J.A., 1979. Groundwater. Englewood Cliffs, NJ, Printice-Hall Inc., 604 p.