
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
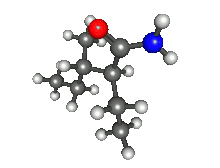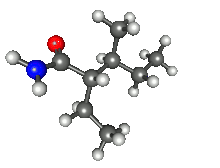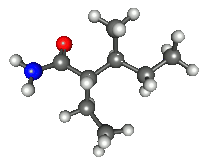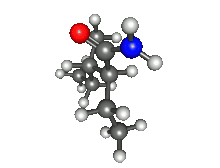
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Ethyl-3-methylpentanamide[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.849 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | valnoctamide |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H17NO | |
| Molar mass | 143.230 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| log P | 1.885 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N05CM13 (WHO) | |
| |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| 94% | |
| Hepatic | |
| 10 hours | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
760 mg kg−1 (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanamides
|
Valpromide |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Valnoctamide (INN, USAN) has been used in France as a sedative-hypnotic since 1964.[2] It is a structural isomer of valpromide, a valproic acid prodrug; unlike valpromide, however, valnoctamide is not transformed into its homologous acid, valnoctic acid, in vivo.[3]
- ^ "valnoctamide - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- ^ Harl, F. M. (March 1964). "[Clinical Study Of Valnoctamide On 70 Neuropsychiatric Clinic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Treatment]". La Presse Médicale (in French). 72: 753–754. PMID 14119722.
- ^ Haj-Yehia, Abdullah; Meir Bialer (August 1989). "Structure-pharmacokinetic relationships in a series of valpromide derivatives with antiepileptic activity". Pharmaceutical Research. 6 (8): 683–689. doi:10.1023/A:1015934321764. PMID 2510141. S2CID 21531402.