| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Vanadium fluoride, Vanadium trifluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.141 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| F3V | |
| Molar mass | 107.9367 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow-green powder (anhydrous) Green powder (trihydrate)[1] |
| Density | 3.363 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 1,395 °C (2,543 °F; 1,668 K) at 760 mmHg (anhydrous) ~ 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) at 760 mmHg (trihydrate) decomposes[1] |
| Boiling point | Sublimes |
| Insoluble[1] | |
| Solubility | Insoluble in EtOH[1] |
| 2.757·10−3 cm3/mol[1] | |
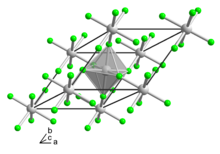
| Structure | |
| Rhombohedral, hR24[2] | |
| R3c, No. 167[2] | |
| 3 2/m[2] | |
a = 5.17 Å, c = 13.402 Å[2] α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 120°
| |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  [3] [3]
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H311, H314, H331[3] | |
| P261, P280, P301+P310, P305+P351+P338, P310[3] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Vanadium(III) chloride Vanadium(III) oxide Vanadium(III) nitride |
Other cations
|
Vanadium(IV) fluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Vanadium(III) fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula VF3. This yellow-green, refractory solid is obtained in a two-step procedure from V2O3.[4] Similar to other transition-metal fluorides (such as MnF2), it exhibits magnetic ordering at low temperatures (e.g. V2F6.4H2O orders below 12 K[5]).
- ^ a b c d e f Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- ^ a b c d Douglas, Bodie E.; Ho, Shih-Ming (2007). Structure and Chemistry of Crystalline Solids. New York: Springer Science+Business Media, Inc. p. 102. ISBN 978-0-387-26147-8.
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Vanadium(III) fluoride. Retrieved on 2014-06-25.
- ^ Sturm, B. J.; Sheridan, C. W. "Vanadium(III) Fluoride" Inorganic Syntheses 1963; Vol. 7, pages 52-54. ISBN 0-88275-165-4.
- ^ S. Nakhal et al., Z. Kristallogr. 228, 347 (2013).doi:10.1524/zkri.2013.1664
