 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Navelbine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a695013 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | intravenous, by mouth[1] |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 43 ± 14% (oral)[3] |
| Protein binding | 79 to 91% |
| Metabolism | liver (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 27.7 to 43.6 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (46%) and kidney (18%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
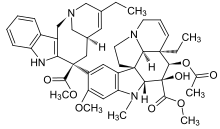
| Formula | C45H54N4O8 |
| Molar mass | 778.947 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Vinorelbine (NVB), sold under the brand name Navelbine among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer.[4] This includes breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.[4] It is given by injection into a vein or by mouth.[4][1]
Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, pain at the site of injection, vomiting, feeling tired, numbness, and diarrhea.[4] Other serious side effects include shortness of breath.[4] Use during pregnancy may harm the baby.[4] Vinorelbine is in the vinca alkaloid family of medications.[1] It is believed to work by disrupting the normal function of microtubules and thereby stopping cell division.[4]
Vinorelbine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1994.[4] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[5][6]
- ^ a b c British national formulary : BNF 69 (69 ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. p. 594. ISBN 9780857111562.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Marty M, Fumoleau P, Adenis A, Rousseau Y, Merrouche Y, Robinet G, et al. (November 2001). "Oral vinorelbine pharmacokinetics and absolute bioavailability study in patients with solid tumors". Annals of Oncology. 12 (11): 1643–1649. doi:10.1023/A:1013180903805. PMID 11822766.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Vinorelbine Tartrate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.