- The volcano system in Iceland that started activity on August 17, 2014, and ended on February 27, 2015, is Bárðarbunga.
- The volcano in Iceland that erupted in May 2011 is Grímsvötn.

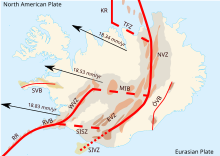
RR, Reykjanes Ridge; RVB, Reykjanes Volcanic Belt; WVZ, West Volcanic Zone; MIB, Mid-Iceland Belt; SISZ, South Iceland Seismic Zone; EVZ, East Volcanic Zone; SIVZ, South Iceland Volcanic Zone; NVZ, North Volcanic Zone; TFZ, Tjörnes Fracture Zone; KR, Kolbeinsey Ridge; ÖVB, Öræfajökul Volcanic Belt; SVB, Snæfellsnes Volcanic Belt.
Volcanoes and volcanic systems in Iceland with Wikipedia articles, Key:
1) Snæfellsjökull, 2) Ljósufjöll, 3) Reykjanes, 4) Svartsengi, 5) Fagradalsfjall, 6) Krýsuvík, 7) Brennisteinsfjöll, 8) Hengill, 9) Surtsey, 10) Eldfell, 11) Eyjafjallajökull, 12) Hekla, 13) Katla, 14) Lakagigar, 15) Öræfajökull, 16) Grímsvötn, 17) Bárðarbunga, 18) Hofsjökull, 19) Langjökull, 20) Askja, 21) Krafla, 22) Þeistareykjabunga
1) Snæfellsjökull, 2) Ljósufjöll, 3) Reykjanes, 4) Svartsengi, 5) Fagradalsfjall, 6) Krýsuvík, 7) Brennisteinsfjöll, 8) Hengill, 9) Surtsey, 10) Eldfell, 11) Eyjafjallajökull, 12) Hekla, 13) Katla, 14) Lakagigar, 15) Öræfajökull, 16) Grímsvötn, 17) Bárðarbunga, 18) Hofsjökull, 19) Langjökull, 20) Askja, 21) Krafla, 22) Þeistareykjabunga

Outlines of central volcanoes in Iceland. Other shading shows: calderas, central volcanoes and fissure swarms, subglacial terrain above 1,100 m (3,600 ft), and seismically active areas. Clicking on the image enlarges to full window and enables mouse-over with more detail.
Iceland experiences frequent volcanic activity, due to its location both on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary, and being over a hotspot. Nearly thirty volcanoes are known to have erupted in the Holocene epoch; these include Eldgjá, source of the largest lava eruption in human history. Some of the various eruptions of lava, gas and ash have been both destructive of property and deadly to life over the years, as well as disruptive to local and European air travel.
