 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /vɒˈrɪnoʊstæt/ vorr-IN-oh-stat |
| Trade names | Zolinza |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607050 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 1.8–11%[1] |
| Protein binding | ~71% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic glucuronidation and β-oxidation CYP system not involved |
| Metabolites | vorinostat O-glucuronide, 4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid (both inactive)[2] |
| Elimination half-life | ~2 hours (vorinostat and O-glucuronide), 11 hours (4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid) |
| Excretion | Renal (negligible) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.207.822 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
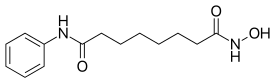
| Formula | C14H20N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 264.325 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Vorinostat (rINN),[3] also known as suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (suberoyl+anilide+hydroxamic acid abbreviated as SAHA), is a member of a larger class of compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases (HDAC). Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI) have a broad spectrum of epigenetic activities.
Vorinostat is marketed under the name Zolinza (/zoʊˈlɪnzə/ zoh-LIN-zə) by Merck for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations in patients with cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) when the disease persists, gets worse, or comes back during or after two systemic therapies.[2][4] The compound was developed by Columbia University chemist Ronald Breslow and Memorial Sloan-Kettering researcher Paul Marks.[5][6]
- ^ "Withdrawal Assessment Report for Vorinostat MSD 100 mg Hard Capsules (vorinostat)" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 23 October 2008. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 September 2016. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ^ a b "Zolinza (vorinostat) Capsules. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USA. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 56" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 20 (3): 232. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 5, 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ^ "ZOLINZA, Merck's Investigational Medicine for Advanced Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma (CTCL), To Receive Priority Review from U.S. Food and Drug Administration" (Press release). Merck & Co. June 7, 2006. Archived from the original on September 14, 2006. Retrieved October 6, 2006.
- ^ Lee JH, Mahendran A, Yao Y, Ngo L, Venta-Perez G, Choy ML, et al. (September 2013). "Development of a histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor and its biological effects". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (39): 15704–15709. Bibcode:2013PNAS..11015704L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1313893110. PMC 3785767. PMID 24023063.
- ^ Marks PA, Breslow R (January 2007). "Dimethyl sulfoxide to vorinostat: development of this histone deacetylase inhibitor as an anticancer drug". Nature Biotechnology. 25 (1): 84–90. doi:10.1038/nbt1272. PMID 17211407. S2CID 12656582.