| Nerve injury | |
|---|---|
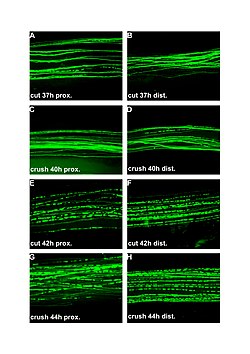 | |
| Fluorescent micrographs (100x) of Wallerian degeneration in cut and crushed peripheral nerves. Left column is proximal to the injury, right is distal. A and B: 37 hours post cut. C and D: 40 hours post crush. E and F: 42 hours post cut. G and H: 44 hours post crush. | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Wallerian degeneration is an active process of degeneration that results when a nerve fiber is cut or crushed and the part of the axon distal to the injury (which in most cases is farther from the neuron's cell body) degenerates.[1] A related process of dying back or retrograde degeneration known as 'Wallerian-like degeneration' occurs in many neurodegenerative diseases, especially those where axonal transport is impaired such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer's disease.[2] Primary culture studies suggest that a failure to deliver sufficient quantities of the essential axonal protein NMNAT2 is a key initiating event.[3][4]
Wallerian degeneration occurs after axonal injury in both the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS). It occurs in the section of the axon distal to the site of injury and usually begins within 24–36 hours of a lesion. Prior to degeneration, the distal section of the axon tends to remain electrically excitable. After injury, the axonal skeleton disintegrates, and the axonal membrane breaks apart. Axonal degeneration is followed by degradation of the myelin sheath and infiltration by macrophages. The macrophages, accompanied by Schwann cells, serve to clear the debris from the degeneration.[5][6]
Schwann cells respond to loss of axons by extrusion of their myelin sheaths, downregulation of myelin genes, dedifferentiation and proliferation. They finally align in tubes (Büngner bands) and express surface molecules that guide regenerating fibers.[7] Within 4 days of the injury, the distal end of the portion of the nerve fiber proximal to the lesion sends out sprouts towards those tubes and these sprouts are attracted by growth factors produced by Schwann cells in the tubes. If a sprout reaches the tube, it grows into it and advances about 1 mm per day, eventually reaching and reinnervating the target tissue. If the sprouts cannot reach the tube, for instance because the gap is too wide or scar tissue has formed, surgery can help to guide the sprouts into the tubes. Regeneration is efficient in the PNS, with near complete recovery in case of lesions that occur close to the distal nerve terminal. However recovery is hardly observed at all in the spinal cord. One crucial difference is that in the CNS, including the spinal cord, myelin sheaths are produced by oligodendrocytes and not by Schwann cells.
- ^ Trauma and Wallerian Degeneration, University of California, San Francisco
- ^ Coleman MP, Freeman MR (1 June 2010). "Wallerian degeneration, wld(s), and nmnat". Annual Review of Neuroscience. 33 (1): 245–67. doi:10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153248. PMC 5223592. PMID 20345246.
- ^ Gilley J, Coleman MP (January 2010). "Endogenous Nmnat2 is an essential survival factor for maintenance of healthy axons". PLOS Biology. 8 (1): e1000300. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000300. PMC 2811159. PMID 20126265.
- ^ Brazill JM, Li C, Zhu Y, Zhai RG (2017). "NMNAT: It's an NAD + Synthase… It's a Chaperone… It's a Neuroprotector". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 44: 156–162. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2017.03.014. PMC 5515290. PMID 28445802.
- ^ Waller A (1 January 1850). "Experiments on the Section of the Glossopharyngeal and Hypoglossal Nerves of the Frog, and Observations of the Alterations Produced Thereby in the Structure of Their Primitive Fibres". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 140: 423–429. doi:10.1098/rstl.1850.0021. JSTOR 108444.
- ^ Coleman MP, Conforti L, Buckmaster EA, Tarlton A, Ewing RM, Brown MC, Lyon MF, Perry VH (August 1998). "An 85-kb tandem triplication in the slow Wallerian degeneration (Wlds) mouse". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (17): 9985–90. Bibcode:1998PNAS...95.9985C. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.17.9985. PMC 21448. PMID 9707587.
- ^ Stoll G, Müller HW (April 1999). "Nerve injury, axonal degeneration and neural regeneration: basic insights". Brain Pathology. 9 (2): 313–25. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.1999.tb00229.x. PMC 8098499. PMID 10219748. S2CID 24140507.