
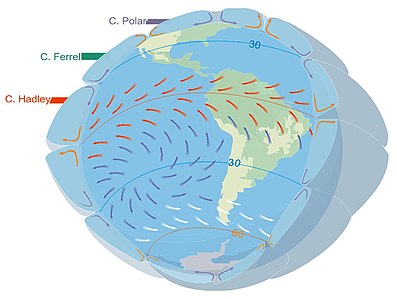
The westerlies, anti-trades,[2] or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about 30 degrees) and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner.[3] Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere.
The westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere (called also 'Brave West winds' at striking Chile, Argentina, Tasmania and New Zealand), in areas where land is absent, because land amplifies the flow pattern, making the current more north–south oriented, slowing the westerlies. The strongest westerly winds in the middle latitudes can come in the roaring forties, between 40 and 50 degrees south latitude. The westerlies play an important role in carrying the warm, equatorial waters and winds to the western coasts of continents, especially in the southern hemisphere because of its vast oceanic expanse.
- ^ Martín, Rodrigo Sebastian (2019-04-28). LA PEQUEÑA EDAD DE HIELO EN PATAGONIA AUSTRAL, estudio de la evolución histórica de las comunidades de quironómidos (Diptera, Chironomidae) en la Laguna Azul, Santa Cruz, Argentina [The Little Ice Age in Southern Patagonia: A Study of the Historical Evolution of Chironomid Communities (Diptera, Chironomidae) in Laguna Azul, Santa Cruz, Argentina.] (PDF) (in Spanish). UBA (published 2022).
- ^ Robert Fitzroy (1863). The weather book: a manual of practical meteorology. Longman, Green, Longman, Roberts, & Green. p. 63.
- ^ "Westerlies". Glossary of Meteorology. American Meteorological Society. 2005. Archived from the original on 2010-06-22. Retrieved 2018-01-22.