| Western Armenian | |
|---|---|
| Արեւմտահայերէն (Arevmdahayerēn) | |
| Native to | Turkey (Armenian Highlands), Armenia, Cyprus, Lebanon, Syria |
Native speakers | 1.6 million (2019)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
| Armenian alphabet (virtually always in the Classical Armenian orthography) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | hyw |
| Glottolog | homs1234 |
| Linguasphere | 57-AAA-ac |
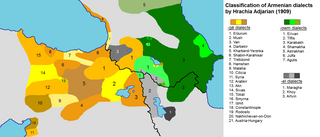 Map of the Armenian dialects in early 20th century: -gë dialects, corresponding to Western Armenian, are in yellow. | |
 Western Armenian is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger[2] | |
 |
| History of the Armenian language |
|---|
|
|
Armenian alphabet Romanization of Armenian |
Western Armenian (Western Armenian: Արեւմտահայերէն, romanized: Arevmdahayeren [ɑɾɛvmədɑhɑjɛˈɾɛn])[a] is one of the two standardized[3] forms of Modern Armenian, the other being Eastern Armenian. It is based mainly on the Istanbul Armenian dialect, as opposed to Eastern Armenian, which is mainly based on the Yerevan Armenian dialect.
Until the early 20th century, various Western Armenian dialects were spoken in the Ottoman Empire, predominantly in the historically Armenian populated regions of Western Armenia. The dialectal varieties of Western Armenian currently in use include Homshetsi, spoken by the Hemshin peoples;[4] the dialects of Armenians in Kessab, Latakia and Jisr al-Shughur in Syria, Anjar in Lebanon, and Istanbul and Vakıflı, in Turkey (part of the "Sueidia" dialect). The Sasun and Mush dialects are also spoken in modern-day Armenian villages such as Bazmaberd and Sasnashen. The Cilician dialect is also spoken in Cyprus, where it is taught in Armenian schools (Nareg), and is the first language of about 3,000 people of Armenian descent.
Forms of the Karin dialect of Western Armenian are spoken by several hundred thousand people in Northern Armenia, mostly in Gyumri, Artik, Akhuryan, and around 130 villages in the Shirak province,[5] and by Armenians in Samtskhe–Javakheti province of Georgia (Akhalkalaki, Akhaltsikhe).[6]
A mostly diasporic language and one that is not an official language of any state, Western Armenian faces extinction as its native speakers lose fluency in Western Armenian amid pressures to assimilate into their host countries. According to Ethnologue, there are 1.58 million native speakers of Western Armenian, primarily in Turkey, Armenia, Georgia, Lebanon, and Iraq. The language is classified as 6b (i.e., threatened, with interruptions in intergenerational transmission).[7]
- ^ Western Armenian at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

- ^ Cite error: The named reference
endangerdcowas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Chahinian, Talar; Bakalian, Anny (1 January 2016). "Language in Armenian American communities: Western Armenian and efforts for preservation". International Journal of the Sociology of Language (237): 37–57. doi:10.1515/ijsl-2015-0034. ISSN 1613-3668. S2CID 147596230.
- ^ Victor A. Friedman (2009). "Sociolinguistics in the Caucasus". In Ball, Martin J. (ed.). The Routledge Handbook of Sociolinguistics Around the World: A Handbook. Routledge. p. 128. ISBN 978-0415422789.
- ^ Baghdassarian-Thapaltsian, S. H. (1970). Շիրակի դաշտավայրի բարբառային նկարագիրը. Bulletin of Social Sciences (in Armenian) (6): 51–60. Archived from the original on 15 September 2019. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ Hovannisian, Richard, ed. (2003). Armenian Karin/Erzerum. Costa Mesa, California: Mazda Publ. p. 48. ISBN 9781568591513.
Thus, even today the Erzerum dialect is widely spoken in the northernmost districts of the Armenian republic as well as in the Akhalkalak (Javakheti; Javakhk) and Akhaltskha (Akhaltsikh) districts of southern Georgia
- ^ "Armenian, Western | Ethnologue Free". Ethnologue (Free All). Retrieved 25 December 2023.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).