| Western India States Agency | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agency of British India | |||||||||||||||
| 1924–1944 | |||||||||||||||
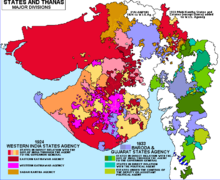 Map of the area of the Western India States Agency and the Baroda and Gujarat States Agency during the British Raj | |||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||
• 1941 | 16,558 km2 (6,393 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||
• 1941 | 5,220,011 | ||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||
• Established | 1924 | ||||||||||||||
• Formation of the Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency | 1944 | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Princely state |
|---|
| Individual residencies |
| Agencies |
|
| Lists |
The Western India States Agency (WISA) was one of the agencies of British India. This agency was formed on 10 October 1924 as a part of the implementation of the Montague Chelmsford report on constitutional reforms. It was formed by merging the areas under the erstwhile Kathiawar, Cutch (covering only Kutch state) and Palanpur agencies.[1]
At one time or another between 1924 and 1944, 435 princely states were included in this agency, roughly covering the present Gujarat state, but only eighteen out of these were salute states. Some 163 Talukas and Estates were included in this Agency: these were mostly petty (e)states, some no larger than a town or village.
- ^ Great Britain India Office. The Imperial Gazetteer of India. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1908.