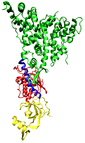
RNA interference (RNAi) is a system within living cells that takes part in controlling which genes are active and how active they are. Two types of small RNA molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific RNAs (mRNA) and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing a messenger RNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic genes – viruses and transposons as well as gene expression in general. The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer (pictured), which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short fragments of ~20 nucleotides that are called siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded (ss) ssRNAs, namely the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded, and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The selective and robust effect of RNAi on gene expression makes it a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can induce suppression of specific genes of interest. (more...)
Recently featured: Hod Stuart – Nathaniel Parker Willis – Blackbeard