| Version of the Windows operating system | |
 | |
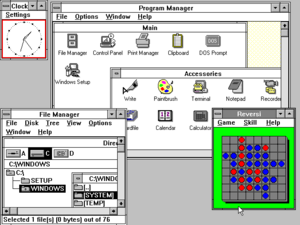 Windows 3.0 screenshot | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Windows |
| Source model | Closed source |
| Released to manufacturing | May 22, 1990 |
| Latest release | 3.00a with Multimedia Extensions / October 20, 1991 |
| License | Commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows 2.1 (1988) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 3.1 (1992) |
| Support status | |
| Unsupported as of December 31, 2001 | |
Windows 3.0 is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, launched on May 22, 1990. It introduces a new graphical user interface (GUI) that represents applications as clickable icons, instead of the list of file names in its predecessors. Later updates expand capabilities, such as multimedia support for sound recording and playback, and support for CD-ROMs.
Windows 3.0 is the first version of Windows to perform well both critically and commercially, and was considered a major improvement over its previous Windows 2.0 offering. Its GUI was considered a challenger to those used and popularized by Apple Macintosh and Commodore Amiga.[1] Other praised features are the improved multitasking, customizability, and especially the utilitarian memory management that troubled the users of Windows 3.0's predecessors.
The software was a major success, achieving 10 million sales. However, Microsoft was criticized by third-party developers for bundling its separate software with the operating environment, which they viewed as an anticompetitive practice. It was succeeded by Windows 3.1 in 1992. Support for Windows 3.0 ended on December 31, 2001.
- ^ Reimer, Jeremy (November 29, 2019). "Half an operating system: The triumph and tragedy of OS/2". Ars Technica. Retrieved November 18, 2024.