| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
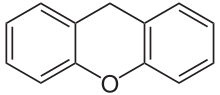
| Preferred IUPAC name
9H-Xanthene[1] | |
| Other names
Dibenzo[a,e]pyran
10H-9-Oxaanthracene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 133939 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.996 |
| EC Number |
|
| 83576 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10O | |
| Molar mass | 182.222 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Melting point | 101 to 102 °C (214 to 216 °F; 374 to 375 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 310 to 312 °C (590 to 594 °F; 583 to 585 K)[2] |
| Hazards[3] | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H317 | |
| P280 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.[4]
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 213. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b Xanthene at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ "Xanthene 99%". Sigma Aldrich.
- ^ Gessner, Thomas; Mayer, Udo (2000). "Triarylmethane and Diarylmethane Dyes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_179. ISBN 978-3527306732.