
| |
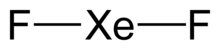
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Xenon difluoride
Xenon(II) fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.850 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| F2Xe | |
| Molar mass | 169.290 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 4.32 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 128.6 °C (263.5 °F; 401.8 K)[2] |
| 25 g/L (0 °C) | |
| Vapor pressure | 6.0×102 Pa[1] |
| Structure | |
| parallel linear XeF2 units | |
| Linear | |
| 0 D | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
254 J·mol−1·K−1[3] |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−108 kJ·mol−1[3] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive to exposed tissues. Releases toxic compounds on contact with moisture.[5] |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H272, H301, H314, H330 | |
| P210, P220, P221, P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P310+P330, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340+P310, P305+P351+P338, P331, P363, P370+P378, P403+P233, P405, P501[4] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | PELCHEM MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Xenon dichloride Xenon dibromide |
Other cations
|
Krypton difluoride Radon difluoride |
Related compounds
|
Xenon tetrafluoride Xenon hexafluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.
It has a nauseating odour and low vapor pressure.[6]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
tramsekwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Hindermann, D. K., Falconer, W. E. (1969). "Magnetic Shielding of 19F in XeF2". J. Chem. Phys. 50 (3): 1203. Bibcode:1969JChPh..50.1203H. doi:10.1063/1.1671178.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ "Sigma Aldrich Xenon Difluoride SDS". Sigma Aldrich. Millpore Sigma. Retrieved 2 November 2022.
- ^ "MSDS: xenon difluoride" (PDF). BOC Gases. Retrieved 2010-06-01.
- ^ James L. Weeks; Max S. Matheson (1966). "Xenon Difluoride". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 8. pp. 260–264. doi:10.1002/9780470132395.ch69. ISBN 9780470132395.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help)
