| Xenophyophorea | |
|---|---|

| |
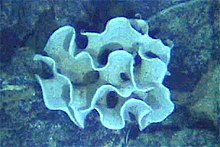
| Image of a deep sea xenophyophore | |
| |
| Xenophyophore at the Galapagos Rift | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Phylum: | Retaria |
| Subphylum: | Foraminifera |
| Class: | Monothalamea |
| Clade: | Xenophyophorea Schulze, 1904 |
| Orders and subtaxa incertae sedis[2] | |
| |
Xenophyophorea /ˌzɛnəˌfaɪəˈfoʊriːə/ is a clade of foraminiferans. Xenophyophores are multinucleate unicellular organisms found on the ocean floor throughout the world's oceans, at depths of 500 to 10,600 metres (1,600 to 34,800 ft).[3][4] They are a kind of foraminiferan that extract minerals from their surroundings and use them to form an exoskeleton known as a test.
They were first described by Henry Bowman Brady in 1883. They are abundant on abyssal plains, and in some regions are the dominant species. Fifteen genera and 75 species have been described, varying widely in size.[5] The largest, Syringammina fragilissima, is among the largest known coenocytes, reaching up to 20 centimetres (8 in) in diameter.[6]
- ^ Tendal, O.S. (1972) A MONOGRAPH OF THE XENOPHYOPHORIA (Rhizopodea, Protozoa)
- ^ Hayward, B.W.; Le Coze, F.; Gross, O. (2019). World Foraminifera Database. Monothalamea. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=744106 on 2019-01-07
- ^ MSNBC Staff (22 October 2011). "Giant amoebas discovered in deepest ocean trench". NBC News. Retrieved 2011-10-24.
- ^ Tendal, O. S. (1972). A Monograph of the Xenophyophoria (Rhizopodea, Protozoa) (Doctoral dissertation). Danish Science Press.
- ^ Gooday, Andrew J.; Holzmann, Maria; Goineau, Aurélie; Pearce, Richard B.; Voltski, Ivan; Weber, Alexandra A.-T.; Pawlowski, Jan (2018-08-03). "Five new species and two new genera of xenophyophores (Foraminifera: Rhizaria) from part of the abyssal equatorial Pacific licensed for polymetallic nodule exploration". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 183 (4): 723–748. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlx093. ISSN 0024-4082.
- ^ Gooday, A.J; Aranda da Silva, A.; Pawlowski, J. (2011). "Xenophyophores (Rhizaria, Foraminifera) from the Nazare Canyon (Portuguese margin, NE Atlantic)". Deep-Sea Research Part II. 58 (23–24): 2401–2419. Bibcode:2011DSRII..58.2401G. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2011.04.005.