| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 21h 04m 55.86s[1] |
| Declination | +43° 55′ 40.272″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.73[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K4:Ib- + A1.5V[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.78[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.66[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | -19.10[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +10.062[1] mas/yr Dec.: +0.861[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.8363 ± 0.1269 mas[1] |
| Distance | 1,150 ± 50 ly (350 ± 20 pc)[1] |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −4.3/+1.3[3] |
| Orbit[5] | |
| Period (P) | 6,750 ± 200 days |
| Semi-major axis (a) | ~766 R☉ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.25 ± 0.07 |
| Inclination (i) | ~50° |
| Details[6] | |
| Primary | |
| Mass | ~8[5] M☉ |
| Radius | 220.09+9.64 −10.56 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 9889±964 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.89 cgs |
| Temperature | 3,878±33 – 4,031 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.26 dex |
| Secondary | |
| Mass | ~2.5[5] M☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
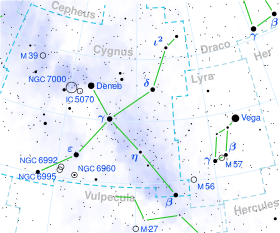
ξ Cygni (Latinised as Xi Cygni) is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation Cygnus, made up of a K-type supergiant star (primary) and an A-type star (secondary). Its apparent magnitude is 3.73, making it readily visible to the naked eye, and it is located around 350 parsecs (1,100 ly) away.
- ^ a b c d e f Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237: 0. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ^ a b Ginestet, N.; Carquillat, J. M. (2002). "Spectral Classification of the Hot Components of a Large Sample of Stars with Composite Spectra, and Implication for the Absolute Magnitudes of the Cool Supergiant Components". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 143 (2): 513. Bibcode:2002ApJS..143..513G. doi:10.1086/342942.
- ^ Famaey, B.; et al. (January 2005), "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 430 (1): 165–186, arXiv:astro-ph/0409579, Bibcode:2005A&A...430..165F, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041272, S2CID 17804304
- ^ a b c Reimers, D.; Schroeder, K.-P. (1989). "Observations of modulation and phase displacement of the stellar wind in six red giant spectroscopic binaries". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 214: 261. Bibcode:1989A&A...214..261R.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
baineswas invoked but never defined (see the help page).