 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hivid (discontinued) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | >80% |
| Protein binding | <4% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 2 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (circa 80%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.677 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
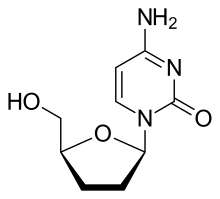
| Formula | C9H13N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 211.221 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Zalcitabine (2′-3′-dideoxycytidine, ddC), also called dideoxycytidine, is a nucleoside analog reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) sold under the trade name Hivid. Zalcitabine was the third antiretroviral to be approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is used as part of a combination regimen.
Zalcitabine appears less potent than some other nucleoside RTIs, has an inconvenient three-times daily frequency and is associated with serious adverse events. For these reasons it is now rarely used to treat human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and it has even been removed from pharmacies entirely in some countries.[1]
- ^ "zalcitabine (CHEBI:10101)". www.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2021-01-18.