 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Brukinsa |
| Other names | BGB-3111 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a620009 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
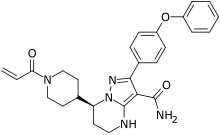
| Formula | C27H29N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 471.561 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Zanubrutinib, sold under the brand name Brukinsa, is an anticancer medication used for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM), marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).[6][10][11][12][13] Zanubrutinib is classified as a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor.[6] It is given by mouth.[6]
It was approved for medical use in the United States in November 2019.[14][10][15][16][17]
- ^ a b "Brukinsa". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 15 October 2021. Archived from the original on 23 October 2021. Retrieved 22 October 2021.
- ^ a b "Brukinsa". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 20 October 2021. Archived from the original on 23 October 2021. Retrieved 22 October 2021.
- ^ "Updates to the Prescribing Medicines in Pregnancy database". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 12 May 2022. Archived from the original on 3 April 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ^ "Brukinsa (Beigene Aus Pty Ltd)". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 5 December 2022. Archived from the original on 18 March 2023. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Brukinsa". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Archived from the original on 30 May 2022. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ a b c d "Brukinsa- zanubrutinib capsule, gelatin coated". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 19 March 2021. Retrieved 1 September 2021.
- ^ "Brukinsa EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 19 July 2021. Archived from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
BeiGene PRwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Zanubrutinib". DrugBank. Archived from the original on 15 November 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
- ^ a b "FDA approves therapy to treat patients with relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma supported by clinical trial results showing high response rate of tumor shrinkage". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 14 November 2019. Archived from the original on 15 November 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Sawalha Y, Bond DA, Alinari L (2020). "Evaluating the Therapeutic Potential of Zanubrutinib in the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Evidence to Date". OncoTargets and Therapy. 13: 6573–6581. doi:10.2147/OTT.S238832. PMC 7351990. PMID 32753893.
- ^ "FDA grants accelerated approval to zanubrutinib for marginal zone lymphoma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 16 September 2021. Archived from the original on 17 September 2021. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "FDA Accepts sNDA for Zanubrutinib to Treat CLL/SLL". AJMC. 23 February 2022. Archived from the original on 28 July 2022. Retrieved 28 July 2022.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Brukinsa". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2019. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ "FDA grants accelerated approval to zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 November 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Drug Trials Snapshots Brukinsa". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 14 November 2019. Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Syed YY (January 2020). "Zanubrutinib: First Approval". Drugs. 80 (1): 91–97. doi:10.1007/s40265-019-01252-4. PMID 31933167. S2CID 210158252.