| Zapotec | |
|---|---|
| Diidxazá, Dizhsa | |
| Ethnicity | Zapotecs |
| Geographic distribution | Oaxaca, Veracruz, Guerrero, Puebla. Small populations in California and New Jersey, United States. |
Native speakers | 490,000 in Mexico (2020 census)[1] |
| Linguistic classification | Oto-Manguean
|
Early form | |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | zap |
| ISO 639-3 | zap |
| Glottolog | zapo1437 |
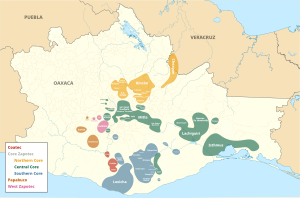 The Zapotec languages as classified by Glottolog | |
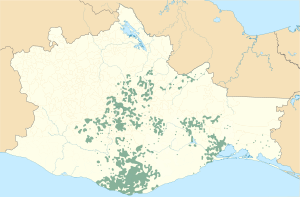 Zapotec speaking areas of Oaxaca (as of 2015) | |
| Notes |
|
The Zapotec /ˈzæpətɛk/[2] languages are a group of around 50 closely related indigenous Mesoamerican languages that constitute a main branch of the Oto-Manguean language family and are spoken by the Zapotec people from the southwestern-central highlands of Mexico. A 2020 census reports nearly half a million speakers,[1] with the majority inhabiting the state of Oaxaca. Zapotec-speaking communities are also found in the neighboring states of Puebla, Veracruz, and Guerrero. Labor migration has also brought a number of native Zapotec speakers to the United States, particularly in California and New Jersey. Most Zapotec-speaking communities are highly bilingual in Spanish.
- ^ a b Lenguas indígenas y hablantes de 3 años y más, 2020 INEGI. Censo de Población y Vivienda 2020.
- ^ Laurie Bauer, 2007, The Linguistics Student’s Handbook, Edinburgh